|
After a brief claim by Spain in 1492 and later Portugal,[3] Barbados became a colony and protectorate of the United Kingdom for over three centuries. The country currently maintains Queen Elizabeth II as head of state. Located at roughly 13° North of the equator and 59° West of the prime meridian, it is considered a part of the Lesser Antilles. Its closest island neighbours are Martinique, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent & the Grenadines to the west. To the south lies Trinidad and Tobago—with which Barbados now shares a fixed official maritime boundary—and also the South American mainland. Barbados's total land area is about 430 square kilometres (166 square miles), and is primarily low-lying, with some higher in the country's interior. The highest point in Barbados is Mount Hillaby in the parish of Saint Andrew. |

Name: Barbados Capital: Bridgetown Population: 284,589 (July 2009 est.) Area: 430 sq km Coastline: 97 km Population density: 648 inhab/ sq Km Religion: Protestant 63.4% (Anglican 28.3%, Pentecostal 18.7%, Methodist 5.1%, other 11.3%), Roman Catholic 4.2%, other Christian 7%, other 4.8%, none or unspecified 20.6% (2008 est.) Lenguage: English Ethnics group: black 90%, white 4%, Asian and mixed 6% Government: parliamentary democracy; independent sovereign state within the Commonwealth Currency: Barbados dollar |
English

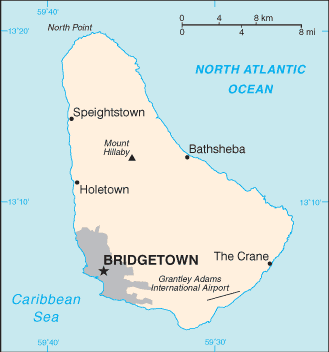 Barbados (pronounced /bɑrˈbeɪdoʊz, bɑrˈbeɪdɒs/), situated just east of the Caribbean Sea, is a West Indian continental island-nation in the western Atlantic Ocean.
Barbados (pronounced /bɑrˈbeɪdoʊz, bɑrˈbeɪdɒs/), situated just east of the Caribbean Sea, is a West Indian continental island-nation in the western Atlantic Ocean.


